Verifying the National Public Data Breach: The Largest Social Security Number Exposure in History
There have been conflicting reports recently published related to the National Public Database (NPD) breach, including claims that “3 billion people have been exposed,” or that “all U.S. social security numbers (SSNs) may have been stolen,” as well as confusion on the quality and veracity of the data.
This blog seeks to clarify and shed light on the real risk and exposure of the breach based on in-depth analysis of the data.
Key highlights of this National Public Data Breach analysis:
- How many people were affected?
Based on our analysis, the total number of unique individuals affected by the breach are:
292 million people were exposed, with 272 million including SSNs
This represents 60% of all historical SSNs issued by the IRS, marking the largest volume of SSN exposure on the dark web to date.
- Who is affected?
The data is outdated and goes back to the beginning when SSNs were first issued in 1936, including deceased individuals. Some insights include:
- Only a small percentage of the SSNs exposed include those assigned within the last 20 years.
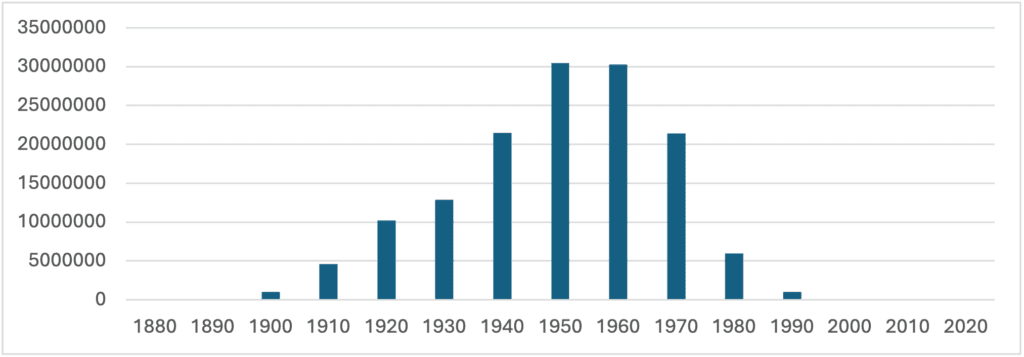
- The larger population affected was born between 1950 and 1970, as shown in the graph below:
- What is the quality of the data?
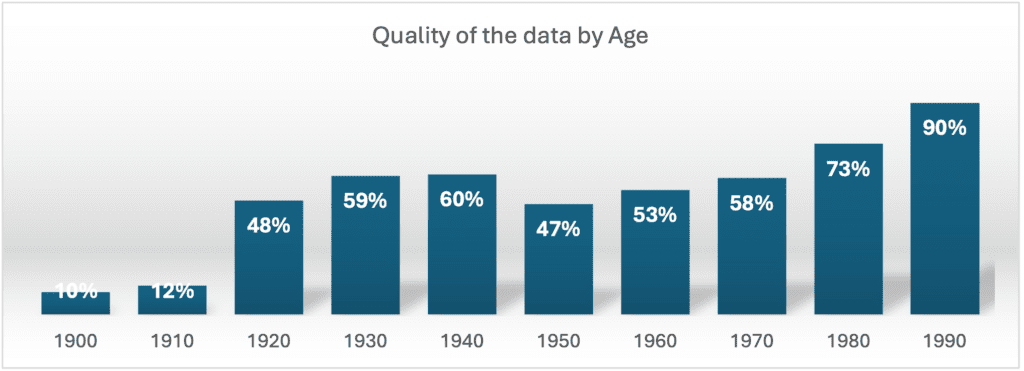
The data comes from a poor collection operation from a mix of sources and includes many errors. We created tests to evaluate information with minimal accuracy that may pose some risk for identity attacks.
49% of the SSNs exposed don’t include the minimum quality to pose a risk for identity attacks
Data is always being updated on an ongoing basis, which most likely explains why the quality changes dramatically depending on the age of the data.
Note that even if there are deceased individuals in the dataset, the highest proportion of actionable information affects the living population.
- What is the magnitude of the risk of this dataset?
Even if only 51% of the SSNs exposed hold a minimal quality to be used in identity attacks, this translates to added risk to an unprecedented 138 million people.
NPD is the largest SSN exposure ever surfaced in the dark web – this breach could be used to attack 138 million people
Again, even though the dataset includes many deceased individuals, the highest proportion of actionable information affects the existing population.
Analysis of the Data
Total SSNs Exposed
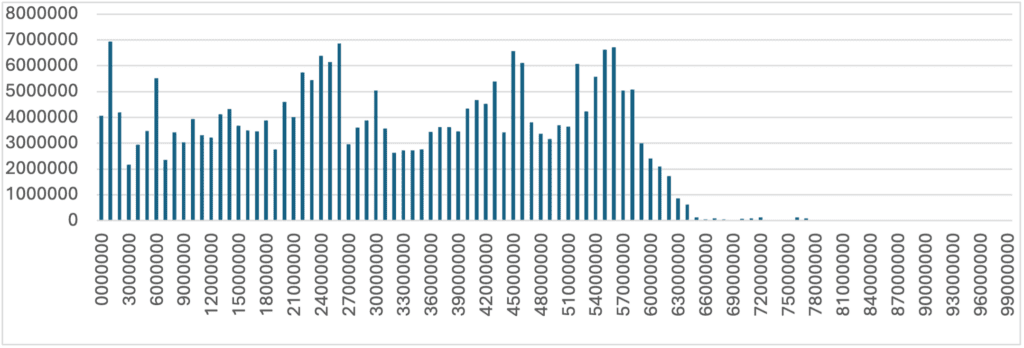
The total unique SSNs from the collision of Part 1 and Part 2 is 272 million. Since each SSN can only be assigned to one person, the total number of people that had their SSNs exposed, if all SSN numbers are true.
The IRS has assigned 453 million from the 1 billion total possible. This means that this dump exposes 60% of the total historical SSNs. The distribution of SSNs is shown below.
Total Number of People Impacted
In the subsequent section, it’s noted that there are 21 million exposed email records not linked to an SSN. Dividing this by 1.1 (the average number of emails per person) reveals an estimated 19 million individuals whose emails were exposed without their SSNs. Adding these 19 million individuals to the 272 million with exposed SSNs, the total number of people affected by the NPD breach amounts to 292 million.
Detailed Numbers
All National Public Data Breach:
- Unique People: 294 million
- Unique SSNs: 272 million
- Unique Emails: 32 million
Detailed information from each package:
- Part 1, also called “partial”:
- Records: 42,084,115
- Unique SSNs: 16,229,269
- Unique emails: 32,052,804
- Unique emails not associated to an SSN: 21,539,497
- Unique SSNs with one or more emails: 10,513,307
- Average number of emails per person: 1.1
- Part 2, also called “full”:
- Records: 261,538,219
- Unique SSNs: 261.538.218
- Emails: 0
- Unique emails: 0
Quality Tests
The data consists of a mix of different sources from scraping of non-public sources according to the class action lawsuit. This has led to concerns regarding the quality of the data with a number of people reporting real findings as well as erroneous ones.
Testing SSNs
The most difficult step when testing the accuracy of SSNs is to have a good quality test dataset. Unlike emails and other credentials, SSNs have rarely been exposed in substantial volumes and are difficult to validate due to their sensitive nature — people generally do not and should not disclose their SSN publicly.
At Constella, we can leverage our extensive experience in protecting millions of identities for nearly 10 years. To assess the validity of SSNs, we gathered 100,000 records containing SSNs that were previously exposed in different breaches and leakages and were tagged as “high confidence” by our Alert Engine.
SSN Numbers Test
Out of the 1 billion potential 9-digit SSN combinations, the IRS has assigned only 46%. Our first test was designed to verify the authenticity of the SSN numbers in isolation, without considering any accompanying information like names, addresses, phones, etc.
76% of the SSNs we tested were found in the NPD data
Minimal Accuracy Test
Despite having a robust test dataset, verifying identity information presents significant challenges, particularly when an email is not included, due to the ambiguity in identity details:
- Names often have variations, such as aliases, abbreviations, or different spellings in surnames. Additionally, individuals may change their surnames due to marriage or other reasons.
For example, in our dataset, a man listed as Miguel Guz*** appeared as Michael Guz*** in the NPD dataset, a woman recorded as Josie So*** was listed as Osie So***, a surname Giess***l appeared as Phillip Giess*** without the final “l”, and a woman named Deborah was referred to as Debra.
- Addresses and phone numbers are also subject to change over time, further complicating the verification process. For this reason, when alerting SSN records it is quite rare to find a full match of an SSN exposed identity and the identity being tested.
Due to these variations, seeking exact matches between the test dataset and the data under review is often not very productive, as perfect alignment of details is rare. However, partial matches of the data can be sufficient for impersonation attacks, or can be completed with other datasets, or used for creating synthetic identities.
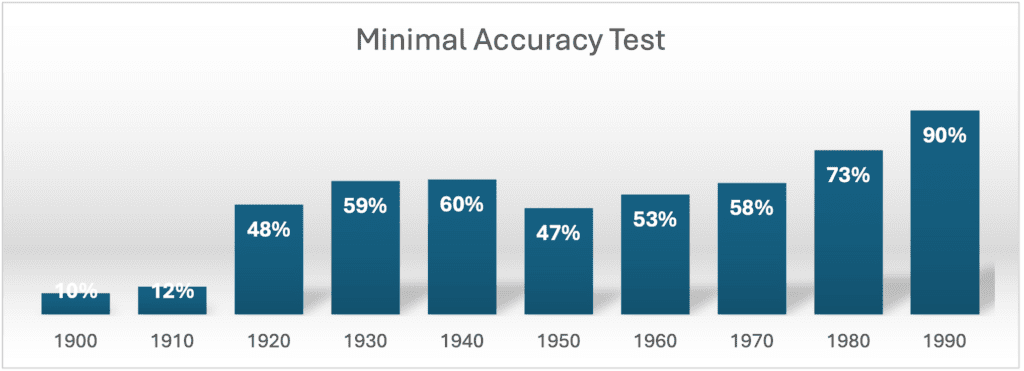
We created tests aimed to evaluate how many of the records include enough real information to pose actual risk of an identity attack. The test evaluates if an SSN, a first name, and a 3rd identity attribute (a surname, DoB, address, or phone) matched. For example: a first name, a surname name and SSN will match the test.
Only 51% of the identities passed the test. But this percentage is highly dependent on the age of the person, being much higher for the younger population. Data from people born in the 90s decade produced a 90% match, from 80s a 73%, and from the 70s a 58% match.
Age of the Data
Only 56% of the records include a Date of Birth. These records contain some “impossible” dates, such as dates of birth in the future or in the first century, affecting a total of 8,900 identities. In analyzing the distribution across decades, the most populated ones are the 1950s and 1960s.
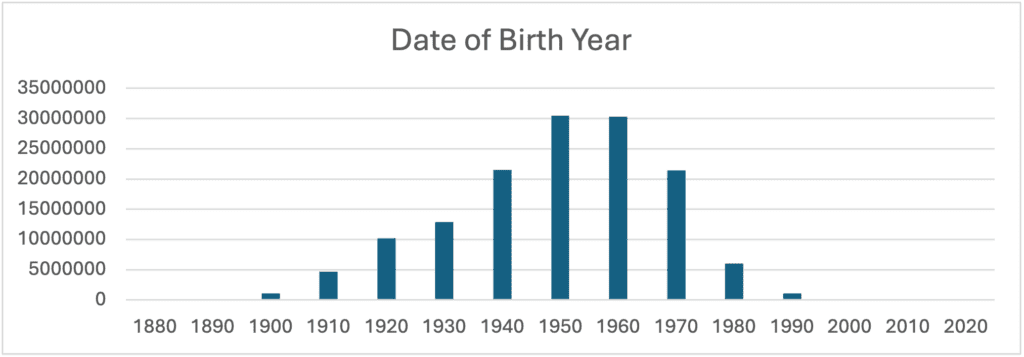
In conclusion, the larger portion of the population was born from 1940 to 1980, the data is quite outdated, with a sharp drop in recent years. It goes way back in the past with 1 million people being born in the 1900’s decade.
About the Breach Package
The breach, initially linked and recently attributed to the data provider National Public Data, was orchestrated by the cybercriminal group USDoD, who allegedly tried to sell the stolen data on the dark web for $3.5 million. This incident underscores the significant risks associated with unauthorized data collection and highlights the critical need for enhanced data protection measures, particularly for individuals in sensitive positions.
The breach first came to light on July 22, 2024, when a malicious actor known as Petrovic an 80GB partial dataset on BreachForums. While this initial leak was considerable, it was merely the tip of the iceberg, revealing only a glimpse of the total compromised data.
By August 6, another hacker named Fenice released the complete dataset, totaling 277GB and 2.69B lines, making this one of the largest data breaches in history.
Versions and Additions. What’s included in our Analysis
On top of the main data, there are additional files with dumps, including a criminal list with 2.8 million criminal records and another one with 2.1 million arrest records.
Some versions of the dump seem to have aggregated other 3rd party leak packages – Troy Hunt reports finding an Acuity directory with 100 million unique emails.
None of them include SSNs, and we won’t include those in this analysis, which will be focused on the core NPD database.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Constella Intelligence authored by Julio Casal. Read the original post at: https://constella.ai/verifying-the-national-public-data-breach/

